CH4 - Job Order Costing
Tuesday, May 28, 2013
1:43 PM
Job order costing
Approach that estimates costs for specific customer orders because the orders may vary from customer to customer.
- Each job will have a cost that is computed by summing the direct and indirect costs of each department or activity that was used to complete the job.
- Therefore averaged over a small number of units
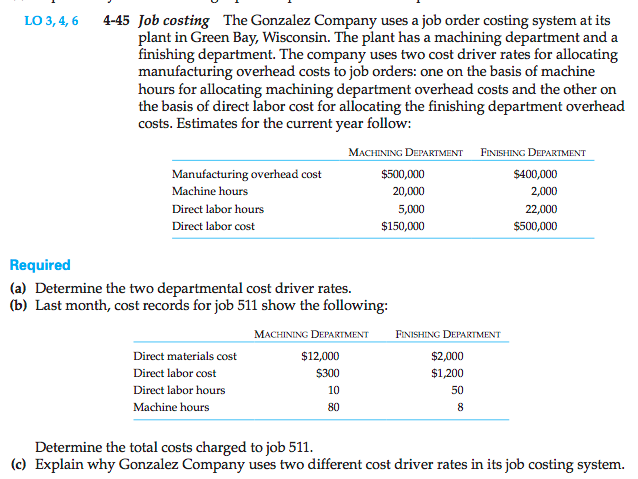
Problem 1
![Machine generated alternative text: 4-43 Job cost, markup, and single rate versus departmental rates Modern
Metaiworks Company has two departments, milling and assembly. The company
uses a job costing system with a plantwide cost driver rate that is computed by
dividing plantwide overhead costs by total plantwide practical capacity direct
labor hours. The following cost and practica] capacity estimates are for October:
Mi AoIMtix
Ovethead costs 5120,000 S 160,000
Direct labor hours 8,000 12,000
Machine hours 12,000 6,000
The following information pertains to job 714, which was started and
completed during October:
MII1i4G A’oI1i
Direct labor hours 10 40
Machine hours 18 8
Direct materials costs $&X) $50
Direct labor sts $100 5600
Required
(a) Determine the cost of job 714.
(b) Suppose that instead of using the plantwide cost driver rate, the company uses machine hours
as the cost driver for applying overhead costs in the milling department, and uses direct labor
hours as the cost driver in the assembly department. Compute these departmental cost driver
rates and determine the cost of job 714 using these rates.
(c) Using the costs you computed in parts a and b, determine the bid price that Modern Metaiworks
will quote under each cost system if it uses a 25% markup on total manufacturing cost.
(d) Provide reasons why Modem Metalworks might prefer the method in part a or the one in part b.](index_files/image001.png)
- Job 714:
Indirect cost rate= (120K+160K)/(8K+12K) = 14
![]()
![]()
= 2250
- Indirect cost rate - Milling = 120K/12K = 10
![]()
![]()
![]()
Total cost = 2263.2
- A: 2812.5
B: 2998.34
- A, less apparent cost means less increase in price, more willing to increase demand.
A is easier to do as well.
Problem 2

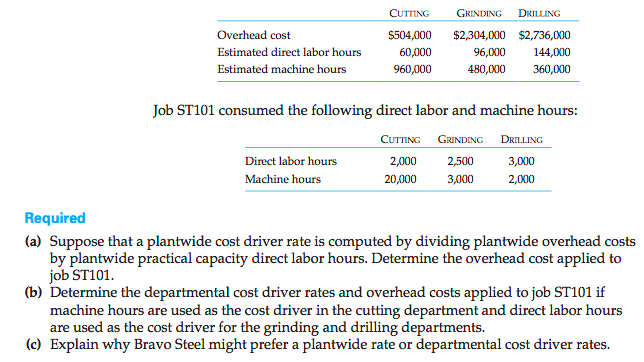
- Will use departmental cost drive rates if the cutting department have a cause-and-effect relationship with machine hours, while those in the grinding and drilling departments have a cause-and effect relationship with direct labour hours.
Problem 3