1 Introduction to Probability
Wednesday, January 04, 2012
11:29 AM
- A simple classification of real world phenomena
- Statistics
- (The science of data)
- Actuarial Science
- Calculating risk
- Computer Science
- OCR
- Engineering
 Random events
Random events - Run the trial only once, any event will either occur or not occur, but not both!
- Repeat the trial many times (under the same set of conditions).
 The relative
frequency of an event.
The relative
frequency of an event.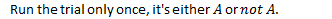
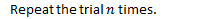
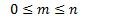
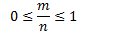
 Frequency
interpretation of prob.
Frequency
interpretation of prob. 
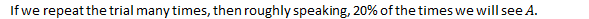
 Subjective prob.
Subjective prob. Classic
definition of prob.
Classic
definition of prob.
![]() Deterministic
Deterministic
Outcomes can be predicted precisely from an initial set of conditions.
"If you give me a set of conditions, I can provide you with the outcome."
Eg) finding the 3rd angle of a triangle.
![]() Random
(Stochastic)
Random
(Stochastic)
Outcomes cannot be predicted precisely from an initial set of conditions.
Eg) Rolling a dice
Many applications:
Implication to daily life.
(Jan 05)
Possible outcomes of a random trial/process/experiment
Eg
Randomly take a hand of 13 cards from a standard deck of 52 (13 Diamonds, 13 Hearts, 13 Spades, 13 Clubs)
A = "The hand consists of all 13 diamonds"
B = "The hand has at least 1 diamond"
Observations
B appears more often than A!
B is more likely to occur!
Definition 1
|
Probability (Prob.) |
A quantitative measurement on how likely a random event will occur under repeated trials. |
![]()
Let
![]()
Let
![]()
![]()
Eg.
Flip a coin.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
0.5
Definition of prob. based on the stability of the relative frequency:
Definition 2
|
Probability
|
|
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
"0.2" has no meaning.
Eg.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Eg.
![]()
![]()
Arbitrary measure of confidence.
Eg.
What is the probability that a terrorist crashed a plane on the twin towers on 9/11?
What is the probability that the moon landing happened?
(A special case of Definition 2; Chapters 2 & 3)