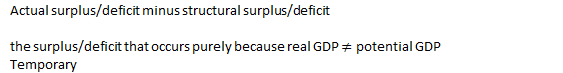Ch 29 - Fiscal Policy
Friday, March 09, 2012
2:35 AM
|
Fiscal Policy |
Government spending/taxing/transferring to achieve macroeconomic objectives |
|
Federal budget |
Amount of government spending and tax revenues |
|
Revenue |
Income tax |
|
Outlays (spending) |
Transfer
payments |
|
Budget Balance |
|
|
Budget surplus |
More revenue |
|
Budget deficit |
More outlays |
|
Balanced budget |
They're equal! |
|
Government debt |
|
Consequences
|
Supply side effects |
Reduce
income |
|
Macroeconomic effects |
Affects the
business cycle. |
|
Real interest rate |
|
|
Real after-tax rate |
|
|
Laffer curve |
|
|
Discretionary fiscal policy |
Initiated by an act of Parliament
|
|
Automatic fiscal policy |
Triggered by the state of the economy
|
|
Government expenditure multiplier |
Magnification
effect of a change in government expenditure on goods on AD |
|
Autonomous tax multiplier |
Magnification
effect a change in autonomous taxes on AD |
|
Balanced budget multiplier |
Effect on AD of a simultaneous change in government expenditure and taxes (that leaves budget balance unchanged) |
Stabilizing business cycle (discretionary)
|
Recessionary gap |
Increase in
government spending |
|
Inflationary gap |
Decrease in
government spending |
Limitations of discretionary fiscal policy
|
Recognition lag |
Time to realized that a policy is needed |
|
Law-making lag |
Passing law takes time |
|
Impact lag |
Effect takes time |
|
Automatic stabilizers |
Without explicit action by government |
|
Induced taxes |
Tax that vary with GDP |
|
Means-tested spending |
Spending according to economic need |
|
Structural surplus or deficit |
Budget balance
that would occur if economy were at full employment (real GDP =
potential) |
|
Cyclical surplus or deficit |
|