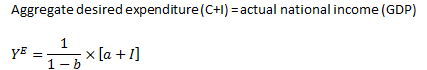Ch 27 - Keynesian Macro Model (I)
Sunday, February 05, 2012
1:00 AM
- Prices stay constant
- No supply constraints
- Increase in read GDP increase aggregate expenditure
- Increase in aggregate expenditure increases real GDP
- Disposable income
- Real interest rates (inverse)
- People consume more when borrowing is cheap
- Wealth
- Expected future income (direct)
- Real interest rate
- Changes in level of sales
- Business confidence
- Autonomous spending
- I, G, X
- Change in MPC
Keynesian Model assumptions:
Expenditure and GDP
|
Induced Expenditure |
Consumption |
|
Autonomous Expenditure |
Investment |
![]()
|
|
Disposable income (spent on consumption or savings) |
|
Y |
Aggregate income |
|
T |
Net taxes |
![]()
|
C |
Consumption |
|
S |
Savings |
![]() Consumption
function
Consumption
function
![]()
|
C |
Consumption |
|
b (aka MPC) |
Marginal propensity to consume |
|
Y |
Income (assuming no taxes) |
![]()
|
MPC |
Ratio of change in consumption and change disposable income |
![]()
|
MPS |
Marginal propensity to save |
![]()
![]()
![]()
|
APC |
Average
propensity to consume |
|
APS |
Average propensity to save |
Move along the consumption function
Shifts consumption function:
![]() Planned
Investment Spending
Planned
Investment Spending
Determinants of aggregate investment expenditure:
|
Real interest rate |
Opportunity cost
of using money for investment in fixed goods |
|
Changes in Sales |
Directly affect stock of inventories |
|
Business confidence |
Direct affect |
![]() Aggregate
Expenditure Function
Aggregate
Expenditure Function
![]()
![]()
|
a |
Autonomous expenditure (when disposable income = 0) |
|
b |
MPC |
|
Equilibrium expenditure |
|
Shifts the AE function:
Changes the slope of AE:
![]() Multiplier
Multiplier
|
Multiplier |
Amount which a change in autonomous expenditure is magnified to determine the change in equilibrium expenditure and real GDP. |
![]()
![]()